CHI’s Roles in Innovation Ecosystems
Purpose: invite participants to reflect on and expand their understand of the value proposition that heritage organisations and practitioners can bring to innovation processes.
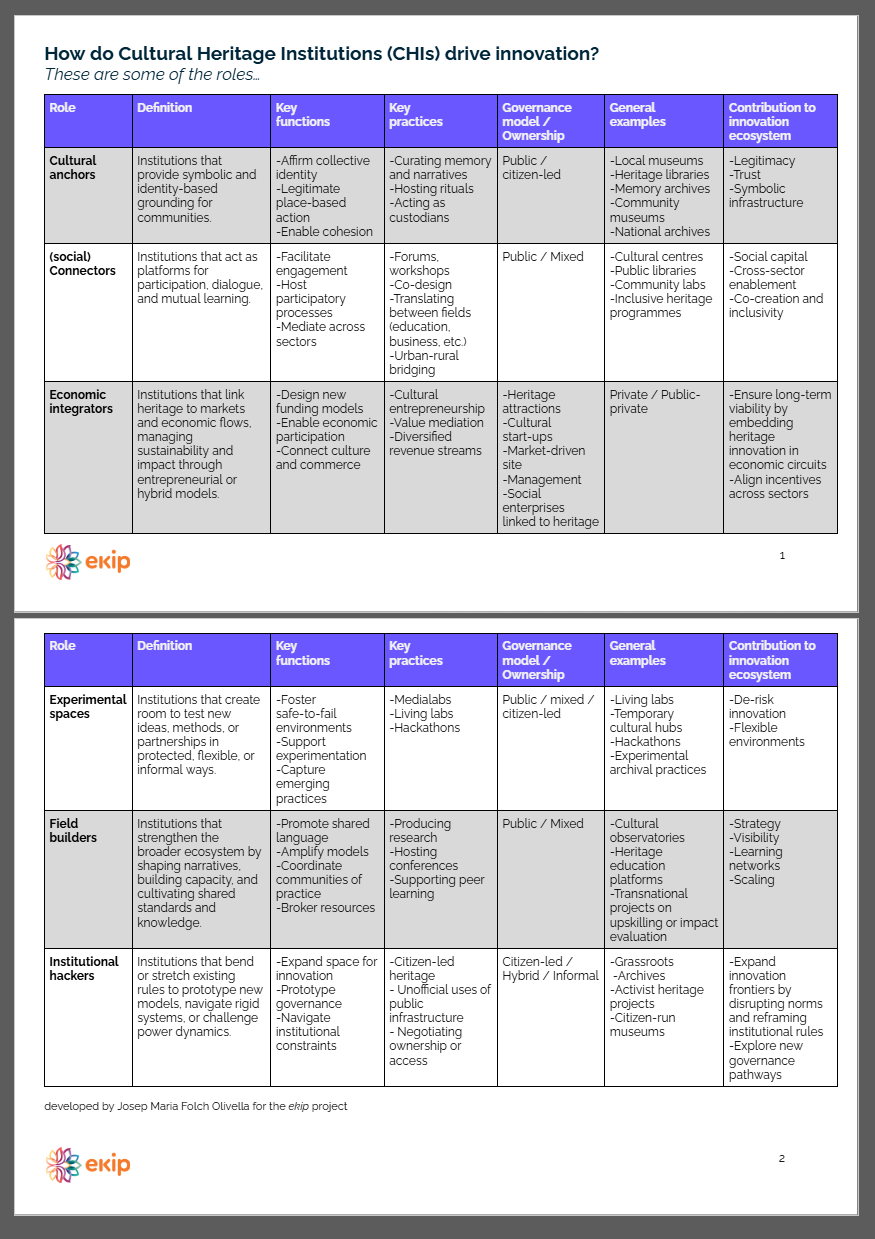
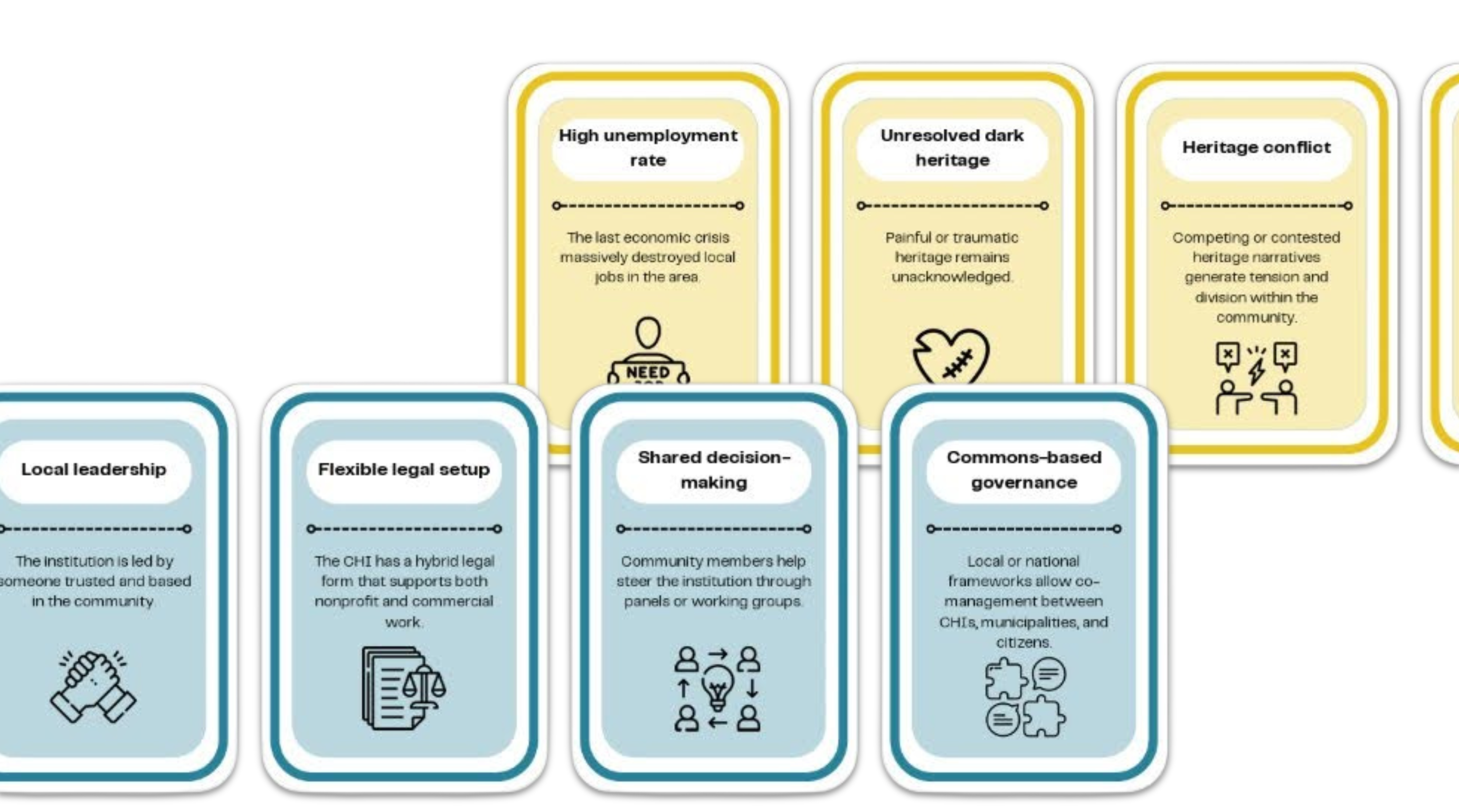
CHIs play a number of different roles in innovation ecosystems. ekip research has introduced a rubric of six innovation roles that CHIs can play:
- Institutional hackers: Institutions that bend or stretch existing rules to prototype new models, navigate rigid systems, or challenge power dynamics.
- Cultural anchors: Institutions that provide symbolic and identity-based grounding for communities.
- (social) connectors: Institutions that act as platforms for participation, dialogue, and mutual learning.
- Economic integrators: Institutions that link heritage to markets and economic flows, managing sustainability and impact through entrepreneurial or hybrid models.
- Experimental spaces: Institutions that create room to test new ideas, methods, or partnerships in protected, flexible, or informal ways.
- Field builders: Institutions that strengthen the broader ecosystem by shaping narratives, building capacity, and cultivating shared standards and knowledge.
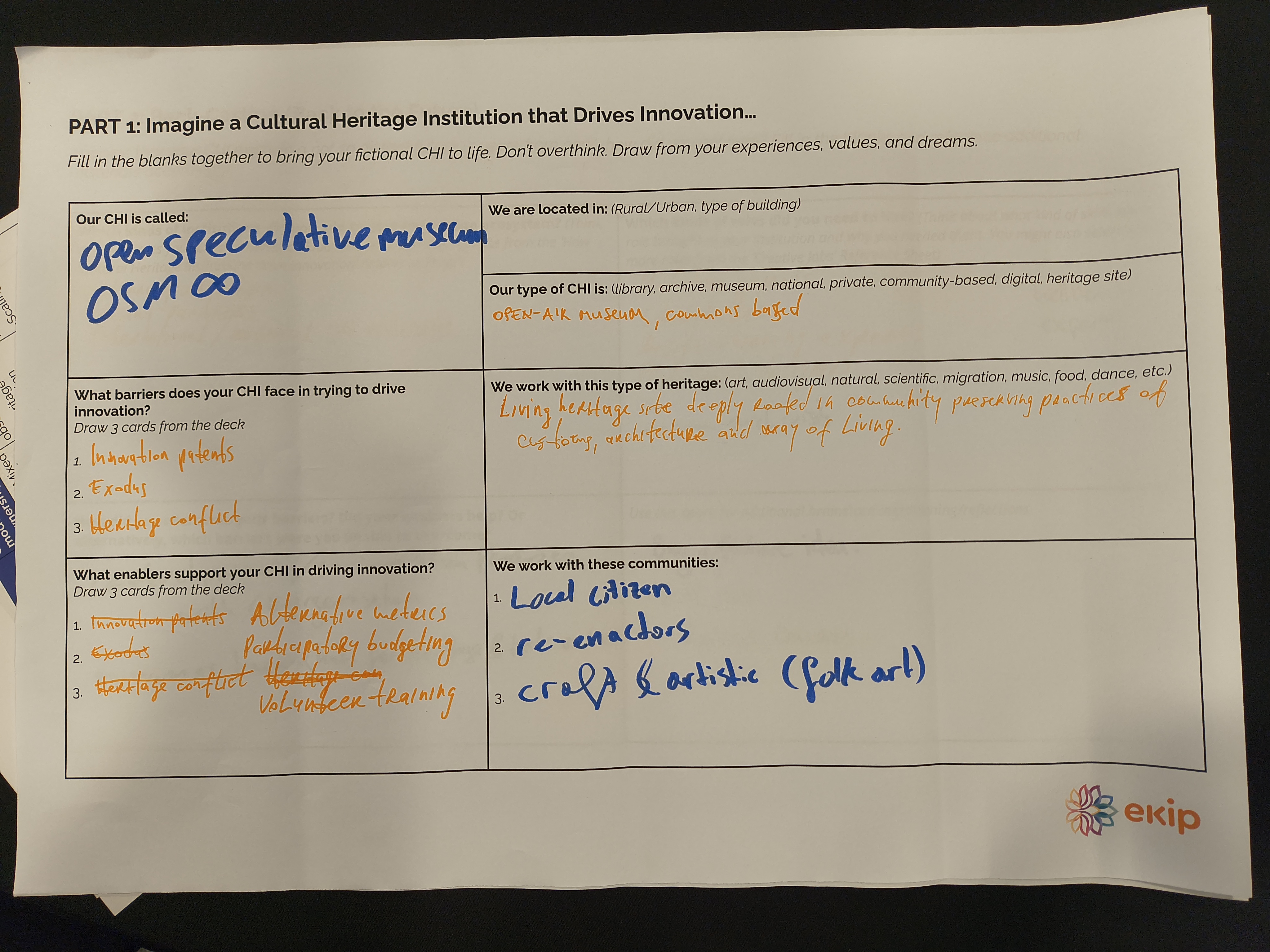
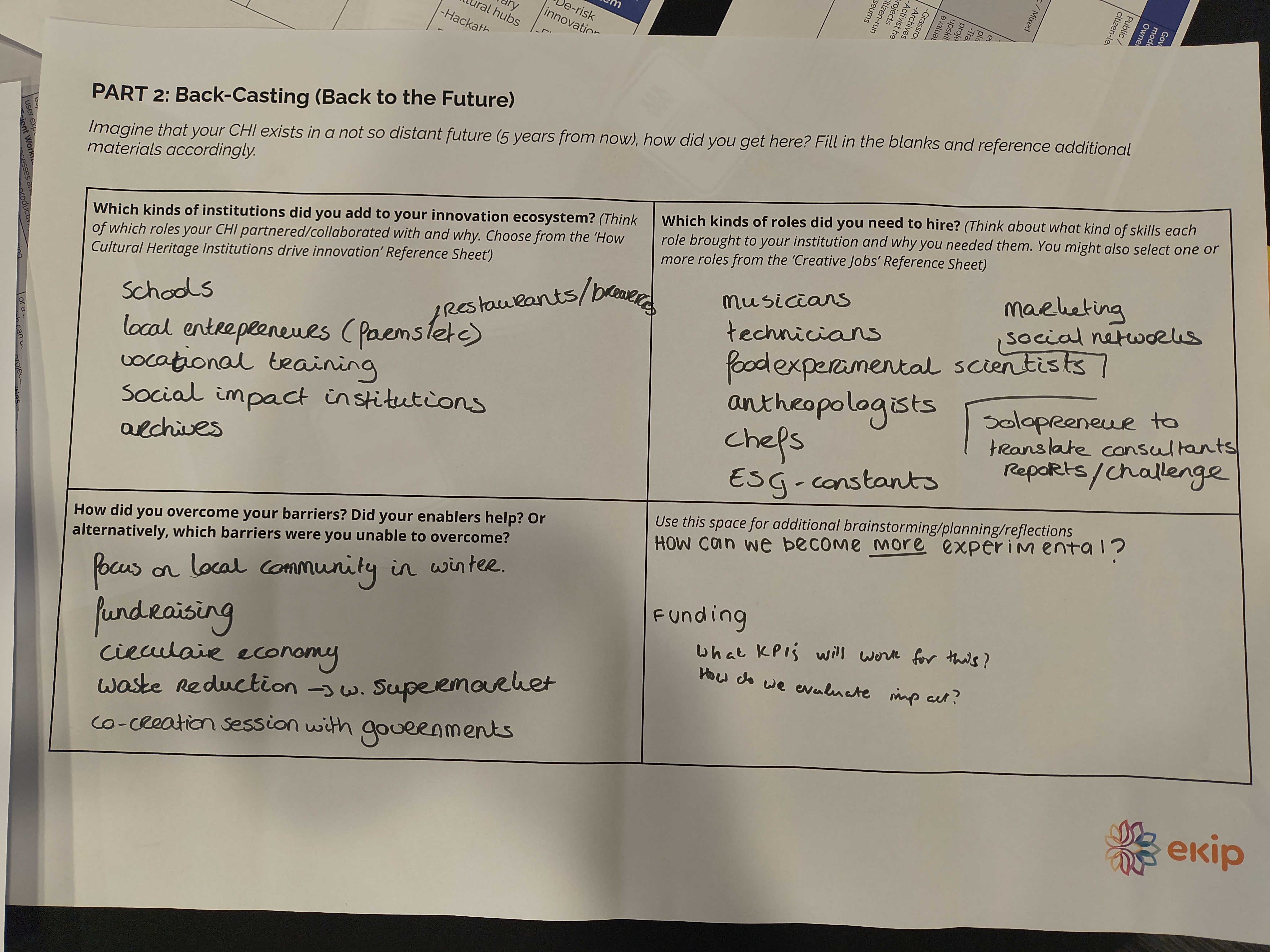
In small groups, participants discussed the key characteristics of each role, then focused on one or two roles as the core basis for imagining their speculative, fictional CHI.